Secured Credit Card vs. Unsecured Credit Card
Understanding the basics: What are secured and unsecured credit cards?
When it comes to credit cards, there are two main types: secured and unsecured credit cards. Understanding the difference between the two is crucial in making informed decisions about your financial future. So, what exactly are secured and unsecured credit cards?
Secured Credit Card: A secured credit card requires a cash deposit as collateral to ensure payment security. The credit limit is usually equal to or a percentage of the deposited amount. This type of credit card is typically recommended for individuals with little to no credit history or for those who want to rebuild their credit. As you responsibly use the secured card and make timely payments, it can help you establish a positive credit history.
Unsecured Credit Card: An unsecured credit card does not require any collateral, making it the more common type. The credit limit is determined by the card issuer based on factors such as your credit score, income, and credit history. Unsecured credit cards are available to individuals with good credit scores and can provide greater flexibility in terms of credit limits and rewards programs.
So, which type of credit card is right for you? It depends on your financial situation and goals. If you have a solid credit history and can qualify for an unsecured credit card, it may offer more advantages such as higher credit limits and rewards. However, if you are new to credit or have a poor credit history, a secured credit card can help you build or rebuild your creditworthiness. Whichever option you choose, it’s important to use credit responsibly, make timely payments, and monitor your spending to maintain good financial health.
Secured Credit Cards
Secured Credit Card definition and how they work
A secured credit card is a type of credit card that requires a cash deposit as collateral to ensure payment security. The deposited amount typically serves as the credit limit or a percentage of it. This means that if you deposit $500, your credit limit will be $500 or a portion of it. Secured credit cards are often recommended for individuals with limited or no credit history, as well as those looking to rebuild their credit.
To obtain a secured credit card, you will need to provide the required cash deposit to the card issuer. This deposit acts as a safeguard for the credit card company in case you fail to make your payments. Your credit activities with the secured card, such as making purchases and paying the bill on time, will be reported to credit bureaus. This can help you establish a positive credit history and improve your credit score over time.
Pros and cons of using a secured credit card
Using a secured credit card has its advantages and disadvantages. Here are some key points to consider:
Pros:
- Opportunity to build credit: With responsible use, a secured credit card can help you establish or improve your credit history.
- Easy qualification: Secured credit cards are more accessible than unsecured cards since they don’t require a good credit score.
- Credit limit control: You have control over your credit limit based on the deposit you make.
Cons:
- Required cash deposit: You need to have funds available to deposit as collateral, which may be a barrier for some individuals.
- Fees and interest rates: Secured credit cards can come with higher fees and interest rates compared to traditional credit cards.
- Limited credit access: Secured credit cards may have restrictions on where they can be used or may not offer the same benefits as unsecured cards.
It’s important to carefully consider your financial situation and goals when deciding whether to use a secured credit card. Properly managing your credit card usage and making timely payments are crucial to building your creditworthiness and achieving long-term financial health.

Unsecured Credit Cards
Unsecured Credit Card definition and how they work
An unsecured credit card is a type of credit card that does not require any collateral or cash deposit. Unlike secured credit cards, which require a cash deposit as collateral for payment security, unsecured credit cards are issued solely based on the borrower’s creditworthiness. The credit limit on an unsecured credit card is determined by the card issuer, and it represents the maximum amount of credit that can be borrowed.
To obtain an unsecured credit card, individuals typically need to meet certain requirements, such as having a good credit score and a stable income. The card issuer assesses the borrower’s creditworthiness based on factors like credit history, income, and debt-to-income ratio. If approved, the borrower will be granted a credit limit and can use the card to make purchases, with the understanding that they will pay back the borrowed amount within the specified time frame.
Pros and cons of using an unsecured credit card
Like any financial tool, unsecured credit cards have their advantages and disadvantages. Here are some key points to consider:
Pros:
- Flexibility: Unsecured credit cards provide more freedom and flexibility to make purchases without the need for a cash deposit.
- Building Credit: By using an unsecured credit card responsibly, borrowers can build a positive credit history and improve their credit score over time.
- Rewards and Benefits: Unsecured credit cards often come with rewards programs, cashback offers, and other benefits that can enhance the cardholder’s experience.
Cons:
- Higher Interest Rates: Unsecured credit cards tend to carry higher interest rates compared to secured credit cards, which can increase the overall cost of borrowing if balances are not paid in full each month.
- Limited Credit Access: Individuals with poor credit may find it difficult to qualify for unsecured credit cards or may be offered lower credit limits.
- Potential Debt Accumulation: Without proper financial discipline, unsecured credit cards can lead to excessive debt if borrowers spend beyond their means.
It is important for individuals considering unsecured credit cards to carefully evaluate their financial situation, prioritize responsible borrowing habits, and make timely payments to avoid interest charges and maintain a healthy credit profile.
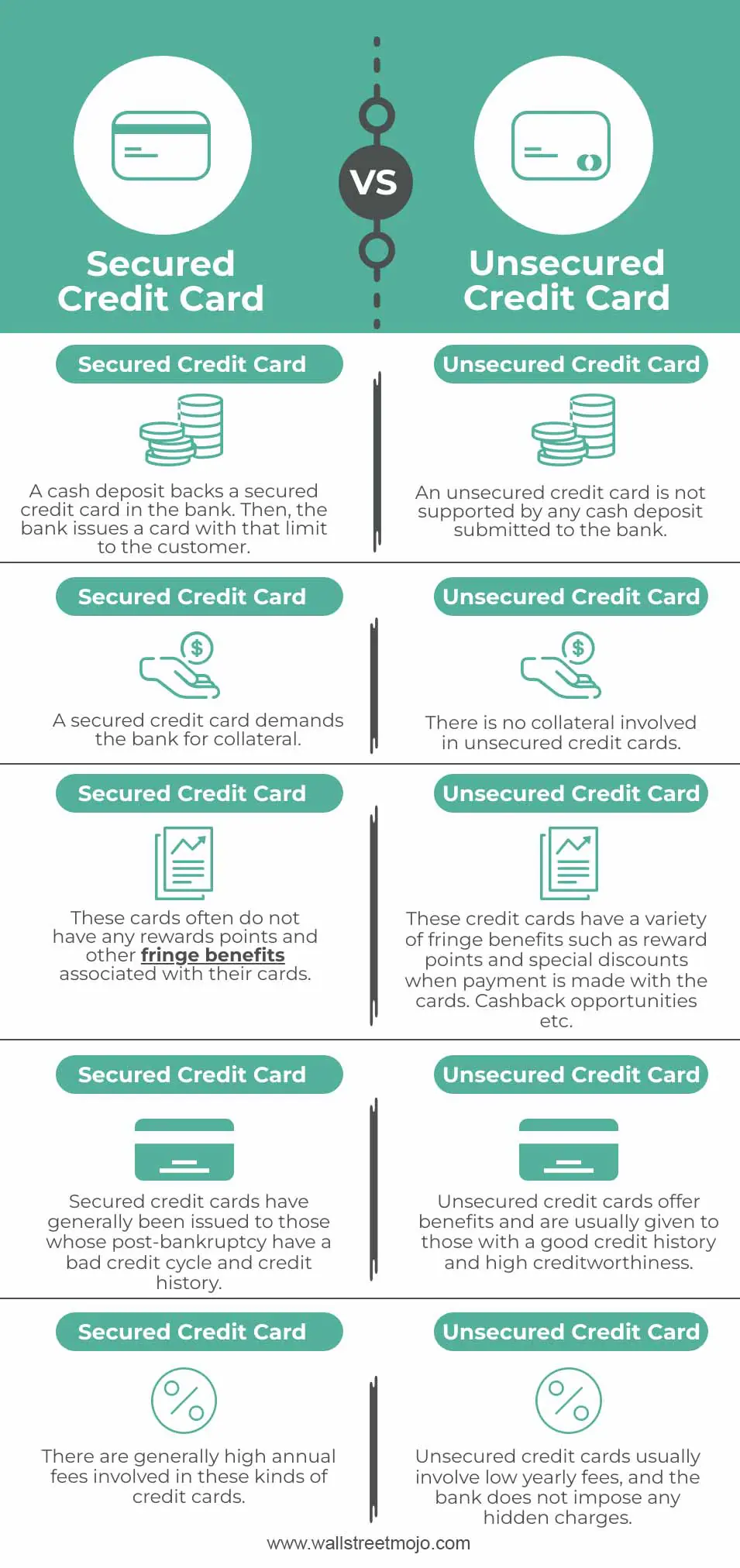
Key Differences between Secured and Unsecured Credit Cards
Security deposit requirement and credit limit
One of the key differences between a secured credit card and an unsecured credit card is the security deposit requirement. With a secured credit card, the cardholder is required to provide a cash deposit as collateral, which acts as a security measure for the card issuer in case the cardholder defaults on their payments. This deposit is typically equal to the credit limit of the card. On the other hand, unsecured credit cards do not require a security deposit. The credit limit on an unsecured credit card is determined solely based on the borrower’s creditworthiness.
Impact on credit score and credit history
Both secured and unsecured credit cards can have an impact on a cardholder’s credit score and credit history. However, the impact may be different. With a secured credit card, responsible payment behavior can help the cardholder build or improve their credit score over time. This is because the cardholder is using their own money as collateral, which reduces the risk for the card issuer. On the other hand, an unsecured credit card can also help build credit, but it requires a higher level of creditworthiness to qualify.
Additionally, the utilization ratio, which is the amount of credit used compared to the total credit limit, can impact credit scores. For secured credit cards, the utilization ratio is typically lower since the credit limit is equal to the security deposit. This can positively impact the cardholder’s credit score. However, for unsecured credit cards, the credit limit is determined by the card issuer and may be lower or higher depending on the borrower’s creditworthiness. It is important for cardholders to keep their utilization ratio low and make timely payments to maintain a positive credit history with both types of cards.
In summary, secured credit cards and unsecured credit cards have key differences in terms of security deposit requirement, credit limit determination, and their impact on credit scores and credit history. It is crucial for individuals to consider their financial situation and credit goals before choosing the type of credit card that best suits their needs.

Choosing the Right Card for You
When it comes to choosing between a secured credit card and an unsecured credit card, there are a few key factors to consider. Understanding these factors can help you make an informed decision about which type of card is best suited to your financial needs and goals.
Factors to consider when selecting between secured and unsecured credit cards
- Security deposit: Secured credit cards require a cash deposit as collateral, while unsecured credit cards do not. If you have the funds available to provide a security deposit, a secured credit card may be a good option for building or rebuilding your credit.
- Credit limit: With a secured credit card, your credit limit is typically equal to the amount of the security deposit. In contrast, the credit limit on an unsecured credit card is determined based on your creditworthiness. If you have a limited credit history or poor credit, a secured card may offer a higher credit limit.
- Interest rates and fees: Compare the interest rates and fees associated with both types of cards. Secured credit cards often have higher interest rates and fees due to the increased risk for the card issuer. However, if you are responsible with your payments, you may be able to transition to an unsecured card with better terms in the future.
Tips for improving your credit and transitioning to an unsecured card
- Make timely payments: Pay your credit card bill on time each month to build a positive payment history. This will demonstrate your creditworthiness to lenders.
- Keep your credit utilization low: Aim to keep your credit card balances below 30% of your credit limit. This shows lenders that you are using credit responsibly and can help improve your credit score.
- Monitor your credit: Regularly check your credit reports for any errors or discrepancies. Disputing inaccuracies can help improve your credit score and increase your chances of qualifying for an unsecured credit card.
Remember, choosing the right card for you depends on your individual financial situation and goals. Consider these factors and tips to make the best decision for building or improving your credit.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash-secured-vs-student-credit-cards-which-to-choose-5190814-Final-78ffa1b9aa5d47028994ff6d47518a2b.jpg)
Conclusion
In conclusion, when choosing between a secured credit card and an unsecured credit card, it is essential to consider various factors to make an informed decision. Factors such as security deposit, credit limit, and interest rates and fees play a significant role in determining which type of card is best suited to your financial needs and goals.
A secured credit card requires a cash deposit as collateral, making it a suitable option for individuals looking to build or rebuild their credit. The credit limit on a secured card is typically equal to the amount of the security deposit, providing a controlled spending limit. However, secured credit cards often come with higher interest rates and fees due to the increased risk for the card issuer.
On the other hand, unsecured credit cards do not require a security deposit and offer a credit limit based on the individual’s creditworthiness. These cards can be beneficial for individuals with good credit history and provide the opportunity to earn rewards and benefits. It is important to compare the interest rates and fees associated with both types of cards to make an educated decision.
To improve credit and transition to an unsecured card, it is crucial to make timely payments, keep credit utilization low, and monitor credit reports for any errors or discrepancies. These steps will showcase responsible credit usage and increase the chances of qualifying for an unsecured credit card with better terms in the future.
Ultimately, the choice between a secured and unsecured credit card depends on individual financial situations and goals. By considering these factors and following the provided tips, individuals can make the best decision for building or improving their credit.
Making an informed decision: Which type of credit card is right for you?
When deciding between a secured credit card and an unsecured credit card, it is important to evaluate your financial situation and goals. Consider factors such as your credit history, ability to provide a security deposit, and desired credit limit. If you have a limited credit history or poor credit, a secured credit card may be a suitable option as it allows you to build or rebuild your credit. However, if you have a good credit history and can manage your credit responsibly, an unsecured credit card with rewards and benefits may be more appealing. It is essential to compare interest rates and fees associated with both types of cards and choose the one that aligns with your financial needs and goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How does a secured credit card work?
A: A secured credit card requires a cash deposit as collateral. The credit limit is typically equal to the amount of the security deposit. It is used to build or rebuild credit, as responsible usage is reported to credit bureaus.
Q: Can I upgrade from a secured credit card to an unsecured credit card?
A: Yes, with responsible credit usage and timely payments, you may be able to transition to an unsecured credit card with better terms in the future. The card issuer may review your creditworthiness and make the decision to upgrade your card.
Q: What is the benefit of an unsecured credit card?A: An unsecured credit card does not require a security deposit and offers a credit limit based on your creditworthiness. It may also provide rewards, benefits, and the opportunity to earn points or cashback on purchases.
Q: How can I improve my credit score?A: Making timely payments, keeping credit utilization low, and monitoring your credit reports for errors can help improve your credit score. Building a positive payment history and responsibly managing your credit will demonstrate creditworthiness to lenders.