Introduction to Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency has been making waves in the financial world, revolutionizing the way we think about money and transactions. In this article, we will explore what cryptocurrency is, how it works, and discuss the benefits and risks associated with it.
What is Cryptocurrency and How Does it Work?
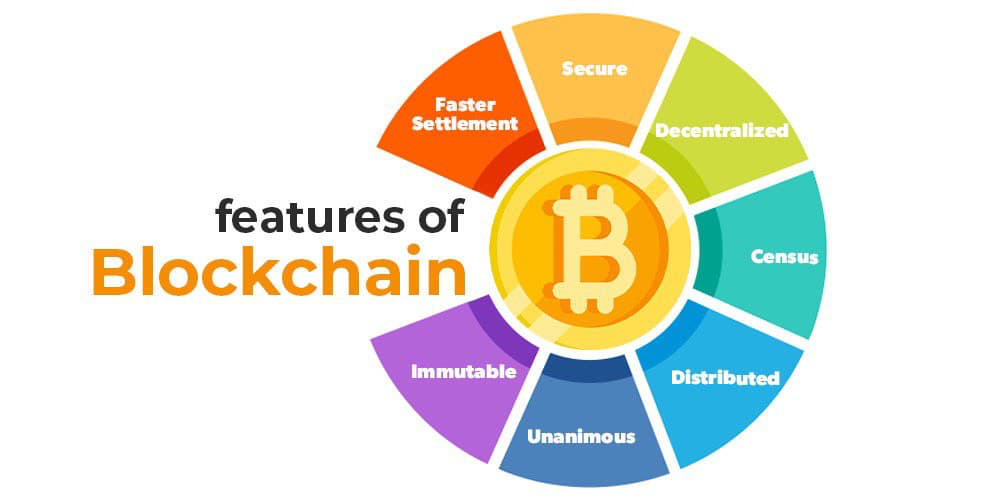
Cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual form of currency that uses cryptography for security. Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments, cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks called blockchains. These blockchains serve as public ledgers that record and verify transactions.
The most well-known cryptocurrency is Bitcoin, which was created in 2009 by an anonymous person or group of people using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. Bitcoin introduced the concept of a peer-to-peer electronic cash system, allowing users to transact directly without the need for intermediaries like banks.
Cryptocurrencies use cryptographic techniques to secure transactions, control the creation of new units, and verify the transfer of assets. Blockchain technology ensures that transactions are transparent, immutable, and resistant to fraud.
Benefits and Risks of Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency offers several benefits that have contributed to its growing popularity:
- Decentralization: Unlike traditional banking systems, cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks. This means that no single authority or institution has control over the currency, making it more resistant to censorship and government interference.
- Security: Cryptocurrencies use cryptographic techniques to secure transactions, making them highly secure and reducing the risk of fraud and hacking.
- Fast and Global Transactions: With cryptocurrencies, transactions can be conducted quickly and easily across borders without the need for intermediaries. This makes it ideal for sending funds globally.
- Financial Inclusion: Cryptocurrencies have the potential to provide financial services to the unbanked populations around the world, giving them access to banking services and empowering them economically.
However, it is important to consider the risks associated with cryptocurrency:
- Volatility: Cryptocurrencies are known for their price volatility, which can make them risky investments. Prices can fluctuate dramatically in short periods, leading to potential losses for investors.
- Lack of Regulation: Cryptocurrencies are currently not regulated by governments or traditional financial institutions. This lack of regulation can make it difficult to resolve disputes and protect investors.
- Security Concerns: While blockchain technology provides strong security, cryptocurrency exchanges and wallets can still be vulnerable to hacking and theft. It is important to use reputable exchanges and take precautions to secure your digital assets.
In conclusion, cryptocurrency is an innovative and disruptive technology that has the potential to shape the future of finance. While it offers several benefits, it also comes with risks. Understanding how cryptocurrency works and being cautious when investing and using digital assets can help navigate the ever-evolving world of cryptocurrencies and ensure a secure and rewarding experience.
Popular Cryptocurrencies
Bitcoin and its Features
Bitcoin is undoubtedly the most well-known cryptocurrency, which paved the way for the whole crypto industry. Created in 2009, it operates on a decentralized network called blockchain. Bitcoin introduced the concept of a peer-to-peer electronic cash system, allowing users to transact directly without intermediaries like banks. Some key features of Bitcoin include:
- Decentralization: Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network, which means it is not controlled by any central authority. This makes it resistant to censorship and government interference.
- Security: Bitcoin transactions are secured using cryptographic techniques, making them highly secure and reducing the risk of hacking and fraud.
- Global Transactions: Bitcoin transactions can be conducted quickly and easily across borders, making it ideal for sending and receiving funds globally.
- Limited Supply: Unlike traditional currencies, Bitcoin has a limited supply of 21 million coins. This scarcity has contributed to its value and appeal as a store of value.
Ethereum and Smart Contracts
Ethereum is another popular cryptocurrency that has gained widespread attention due to its ability to execute smart contracts. It was introduced in 2015 to expand the capabilities of blockchain technology beyond traditional transactions. Ethereum’s key feature is its support for decentralized applications (dApps) and the execution of smart contracts.
- Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They automatically execute when predefined conditions are met. Ethereum revolutionized the concept of smart contracts, enabling developers to create and execute decentralized applications without third-party involvement.
- DApps: Ethereum’s platform allows developers to build and deploy decentralized applications. These applications operate on the blockchain and offer various functionalities, including finance, gaming, and decentralized exchanges.
- Tokenization: Ethereum also enables the creation of new cryptocurrencies or tokens on its platform. This has led to the boom of Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs), where startups raise funds by selling tokens to investors.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Ethereum has played a significant role in the development of decentralized finance. DeFi aims to create a financial system that operates without traditional intermediaries, providing services such as lending, borrowing, and trading on the blockchain.
In conclusion, Bitcoin and Ethereum are two popular cryptocurrencies that have revolutionized the financial industry. Bitcoin introduced the concept of a decentralized, peer-to-peer electronic cash system, while Ethereum expanded the capabilities of blockchain technology through smart contracts and decentralized applications. Understanding the features and potential of these cryptocurrencies can help investors and users navigate the ever-changing world of digital assets and decentralized finance.
Understanding Smart Contracts
What are Smart Contracts and How Do They Work?
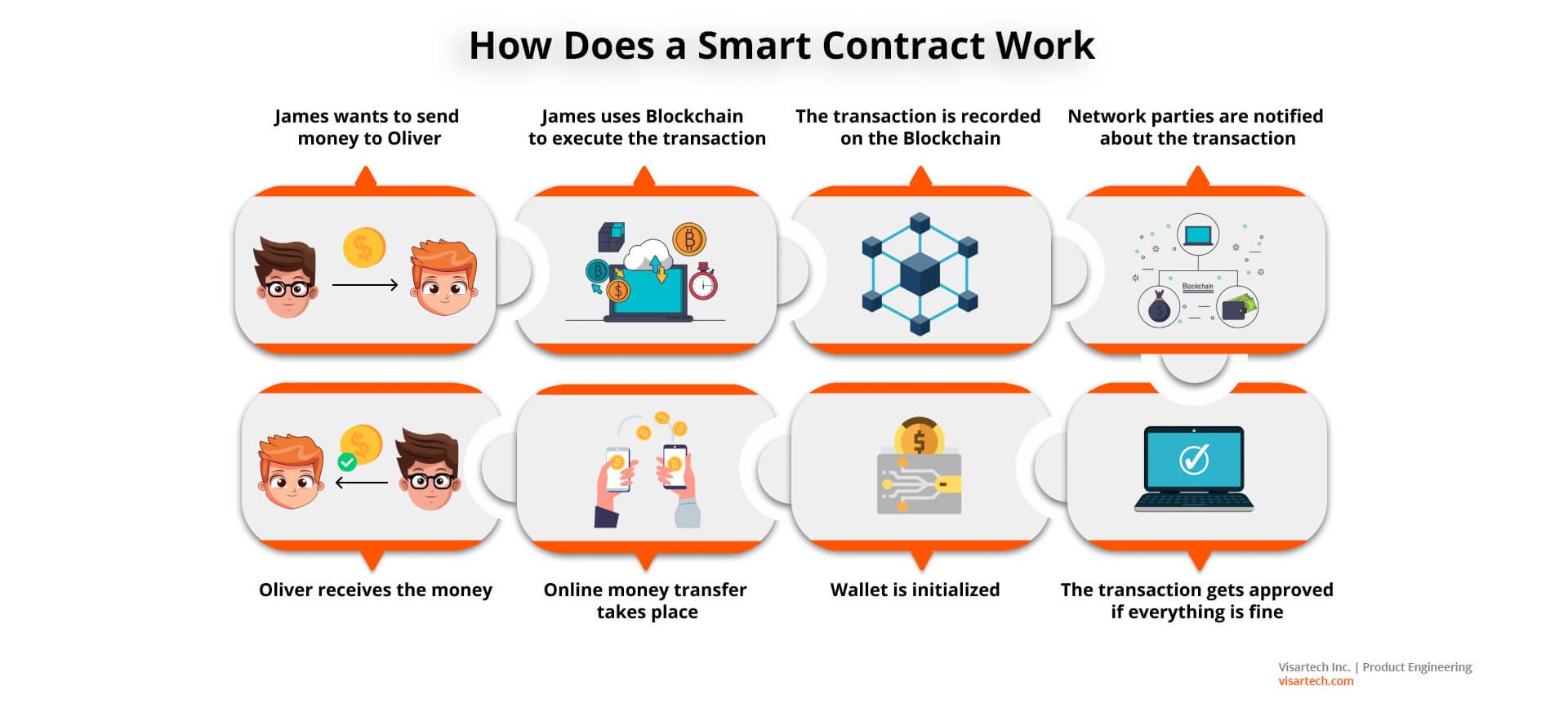
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. These contracts automatically execute when predefined conditions are met. They enable secure, tamper-proof transactions and eliminate the need for intermediaries like lawyers or brokers.
Smart contracts operate on blockchain technology, which is a decentralized, transparent, and immutable digital ledger. The blockchain ensures that every transaction recorded in the smart contract is verifiable and cannot be altered or tampered with.
The execution of smart contracts is based on if-then statements. Once the conditions specified in the contract are met, the contract executes itself and performs the actions stated in the code. For example, if a certain date is reached, the contract can automatically transfer ownership of a property or release funds to a specific party.
Furthermore, smart contracts can interact with other smart contracts, creating complex, interconnected systems. This feature allows for the development of decentralized applications (dApps) that operate independently of any central authority.
Advantages and Limitations of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts offer several advantages over traditional contracts:
- Security: The use of cryptographic techniques ensures that smart contracts are secure and tamper-proof. Once a smart contract is deployed on the blockchain, it cannot be altered without the consensus of the network participants.
- Efficiency: Smart contracts automate the execution and enforcement of contractual obligations, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing administrative costs and delays.
- Transparency: As smart contracts operate on a decentralized blockchain, all transactions are recorded and visible to all participants. This transparency enhances trust and can help prevent fraud.
- Accuracy: Smart contracts are executed based on predefined code, reducing the risk of human error or misinterpretation of contract terms.
Despite their advantages, smart contracts also have some limitations:
- Immutability: Once deployed on the blockchain, smart contracts cannot be easily modified or terminated. This lack of flexibility can be disadvantageous in situations where contract terms need to be renegotiated.
- Complexity: Developing and understanding smart contracts requires technical expertise, which can be a barrier for non-technical individuals or organizations.
- Legal Uncertainty: The legal status of smart contracts varies across jurisdictions. Some legal systems have not yet fully defined the enforceability of smart contracts, which can create uncertainty and hinder widespread adoption.
Despite these limitations, the benefits of smart contracts, such as increased security, efficiency, and transparency, are driving their adoption in various industries. As the technology matures and regulatory frameworks catch up, smart contracts have the potential to revolutionize how contracts are executed and enforced.

Impact of Cryptocurrency and Smart Contracts
Impact of Cryptocurrency on Traditional Financial Systems
Cryptocurrency has become a disruptive force in the traditional financial world, revolutionizing the way transactions are conducted. It offers several key advantages over traditional payment systems:
- Decentralization: Cryptocurrencies operate on a decentralized network, removing the need for intermediaries such as banks. This decentralization grants users more control over their funds and reduces the risk of fraud or manipulation by financial institutions.
- Security: Cryptocurrencies utilize cryptographic techniques to secure transactions, protecting them from hacking or unauthorized access. This ensures the integrity and privacy of financial transactions.
- Lower Transaction Fees: Cryptocurrency transactions often have lower fees compared to traditional financial systems, especially for international transfers. This makes it cost-effective for individuals and businesses to send and receive funds globally.
- Financial Inclusion: Cryptocurrencies have the potential to provide financial services to the unbanked and underbanked populations who do not have access to traditional banking services. By using a smartphone and an internet connection, individuals can participate in the global economy and gain access to financial services.
Applications and Potential of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts, built on blockchain technology, have the potential to transform various industries by automating processes and increasing transparency. Here are some key applications of smart contracts:
- Supply Chain Management: Smart contracts can track and verify the movement of goods throughout the supply chain. This ensures transparency, reduces fraud, and increases efficiency by automating processes such as inventory management, shipping, and payments.
- Real Estate: Smart contracts can streamline the process of buying, selling, and renting properties by eliminating the need for intermediaries, such as lawyers or brokers. They can automatically execute transactions once conditions are met, ensuring faster and more secure real estate transactions.
- Insurance: Smart contracts can automate insurance claims and policy management processes. Claims can be automatically verified, and payouts can be executed once predetermined conditions are met, reducing the administrative burden and improving efficiency.
- Intellectual Property: Smart contracts can help protect intellectual property rights by automatically enforcing licensing agreements and royalty payments. This reduces the risk of infringement and ensures that creators are fairly compensated for their work.
While the potential of cryptocurrency and smart contracts is vast, there are still some challenges to overcome. Regulatory frameworks need to be established to ensure consumer protection, prevent fraud, and define the legal status of cryptocurrencies and smart contracts. Additionally, scalability issues and energy consumption associated with blockchain technology need to be addressed for widespread adoption.
In conclusion, cryptocurrency and smart contracts are reshaping traditional financial systems and revolutionizing various industries. Their decentralized nature, enhanced security, cost-effectiveness, and automation capabilities offer significant benefits. As the technology continues to evolve and regulatory frameworks mature, we can expect further innovation and adoption in the coming years.
Challenges and Future Trends
Challenges in Adopting Cryptocurrency and Smart Contracts
As cryptocurrency and smart contracts continue to gain traction, there are several challenges that need to be addressed for widespread adoption.
Regulatory Frameworks: One of the main challenges is the absence of clear regulatory frameworks governing cryptocurrencies and smart contracts. Governments around the world are working to establish laws and regulations to ensure consumer protection, prevent fraud, and define the legal status of these technologies. Clear guidelines will provide confidence to businesses and individuals to embrace and utilize cryptocurrencies and smart contracts.
Scalability: Scalability is another pressing issue. Blockchain technology, which underlies cryptocurrencies and smart contracts, faces limitations in terms of transaction speed and capacity. As more users join the network, scalability becomes a critical concern. Efforts are being made to develop new consensus mechanisms and improve the scalability of blockchain networks to handle a larger volume of transactions.
Energy Consumption: The environmental impact of blockchain technology is another challenge. The energy consumption required for mining and verifying transactions is significant. Finding sustainable and energy-efficient solutions will be crucial for long-term adoption.
Cybersecurity: Ensuring the security of cryptocurrency transactions and smart contract executions remains a challenge. Hacking incidents and vulnerabilities can lead to financial losses and erode trust in these technologies. Continuous efforts to improve cybersecurity measures, such as secure coding practices and robust encryption algorithms, are necessary to mitigate these risks.
Emerging Trends in the Cryptocurrency and Smart Contract Space
Despite the challenges, the future looks promising for cryptocurrency and smart contracts. Here are some emerging trends to watch out for:
Increased Institutional Adoption: Institutional investors are beginning to recognize the potential of cryptocurrencies as an asset class. This increased interest from institutions, such as banks and hedge funds, brings credibility and liquidity to the market, contributing to its further growth.
DeFi and Decentralized Exchanges: Decentralized Finance (DeFi) platforms and decentralized exchanges (DEXs) are gaining popularity. These platforms leverage smart contracts to enable peer-to-peer lending, trading, and other financial activities without the need for intermediaries. DeFi offers opportunities for financial inclusion and access to financial services for individuals who are underserved by traditional banking systems.
Central Bank Digital Currencies: Central banks around the world are exploring the concept of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs). CBDCs could provide governments with greater control over monetary policy while offering the benefits of fast and secure digital transactions to individuals and businesses.
NFTs and Digital Assets: Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) have gained significant attention recently. NFTs allow for the ownership and trading of unique digital assets, such as artwork, collectibles, and virtual real estate. This market has opened up new possibilities for creators and collectors, revolutionizing the concept of ownership in the digital world.
In conclusion, while there are challenges to overcome, the adoption of cryptocurrency and smart contracts is steadily progressing. Clear regulatory frameworks, improved scalability, enhanced cybersecurity measures, and sustainable energy solutions are key areas of focus. The emerging trends of increased institutional adoption, DeFi platforms, CBDCs, and NFTs indicate the growing acceptance and innovation within the cryptocurrency and smart contract space. As these technologies mature, we can expect further advancements and integration into various industries.

Conclusion
In conclusion, cryptocurrency and smart contracts present both challenges and future trends in the world of finance and technology. Despite the obstacles of unclear regulatory frameworks, scalability issues, energy consumption, and cybersecurity vulnerabilities, the adoption of these technologies is steadily progressing.
Summary of the Key Points
Clear regulatory frameworks are necessary to ensure consumer protection and define the legal status of cryptocurrencies and smart contracts. Efforts are being made by governments worldwide to establish these guidelines and provide confidence to businesses and individuals.
Scalability remains a pressing issue for blockchain networks. As more users join the network, the speed and capacity of transactions become a critical concern. Continual improvement and development of new consensus mechanisms are essential to address this limitation.
The environmental impact of cryptocurrency mining and transaction verification is a challenge that needs to be addressed. Finding sustainable and energy-efficient solutions will be crucial for the long-term adoption of these technologies.
Ensuring the security of cryptocurrency transactions and smart contract executions is of utmost importance. Continuous efforts to improve cybersecurity measures, such as secure coding practices and robust encryption algorithms, are necessary to mitigate the risks associated with hacking incidents and vulnerabilities.
Potential of Cryptocurrency and Smart Contracts in the Future
Despite the challenges, the future of cryptocurrency and smart contracts holds great promise. Several emerging trends indicate the growing acceptance and innovation in this space.
Increased institutional adoption of cryptocurrencies as an asset class brings credibility and liquidity to the market, contributing to its further growth. Institutional investors, such as banks and hedge funds, are beginning to recognize the potential of these digital assets.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) platforms and decentralized exchanges (DEXs) are gaining popularity. These platforms leverage smart contracts to enable peer-to-peer lending, trading, and other financial activities without the need for intermediaries. They offer opportunities for financial inclusion and access to financial services for individuals who are underserved by traditional banking systems.
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) are being explored by central banks around the world. CBDCs could provide governments with greater control over monetary policy while offering fast and secure digital transactions to individuals and businesses.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) have recently gained significant attention. NFTs allow for the ownership and trading of unique digital assets, such as artwork, collectibles, and virtual real estate. This market has opened up new possibilities for creators and collectors, revolutionizing the concept of ownership in the digital world.
As these technologies mature and overcome the challenges they face, we can expect further advancements and integration into various industries. The potential of cryptocurrency and smart contracts to revolutionize finance and create new opportunities is exciting, and businesses and individuals should stay informed about the developments in this rapidly evolving field.